Many folks from all walks of life and occupations aspire on a daily basis to gain a foothold into the new found world of Infosec, cyber security and hacking as that field continues to explode before their eyes at an exponential rate with opportunities and higher paid jobs tempting the uninitiated. As many in the field will tell you, Infosec and cyber security are frontier territory with many new and earlier unimaginable venues and opportunities opening up for entry-level would be adherents.
“Talk is cheap, show me the code ― Linus Torvalds
Computer Program Definition
As defined by Wikipedia:
A computer program is a collection of instructions that can be executed by a computer to perform a specific task.
Although this definition sounds almost too simplistic it speaks volumes in so far as trying to explain a vast and expansive field of study. An ocean of learning awaits those who would take on this seemingly Herculean task.
Background
Python is a widely used and wildly popular high-level programming language used in the many fields such as Data Science, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Cyber Security. Few languages can compare to its meteoric rise across software and mathematical analysis domains in speed and functionality. It was initially developed by Guido van Russum back in 1991 and has been developed further by the Python Software Foundation.
Work on Python began in the late 80s when Guido van Rossum was working at the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) situated in the Netherlands. Begun as a hobby project it was a successor to the ABC programming language. Having helped to create the ABC programming Guido decided to take the syntax and best features of ABC into a new scripting language and worked to iron out all of ABC’s existing user complaints and flaws during the transition. He named the language “Python” after his favorite BBC TV show “Month Pythons Flying Circus”. The Python language was released in 1991 and Guido van Rossum remained the permanent “Benevolent dictator for life” (BDFL) until 2018 when he stepped down. Compared to other high-level languages such as Java, C++ and C, Python used a lot fewer codes and focused on providing readability and developer productivity out of the gate.
The graphic below clearly outlines the rise of Python (thru to 2019).
Why Python? Why now?
Beyond necessary skills in networking and operating systems the greatest asset for anyone entering the InfoSec space is knowledge of programming. Specifically, the knowledge of Python. This will put you in a great place to exercise both your hacking skills and learn from the best proponents in the field.
-
Although some people may have cringed at the idea of getting into programming (and the associated math) that gets over their heads from earlier bitter experiences in high school (or elsewhere), programming in and of itself can be a very rewarding pursuit both within cyber security field and other domains. This skill is transferable!
-
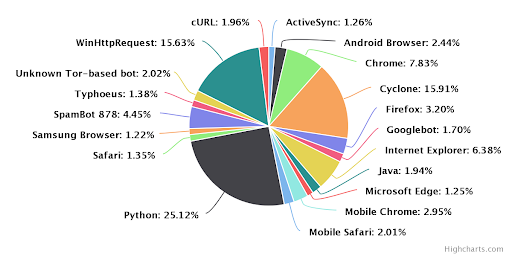
Python through no accident of itself has become the language of choice for hackers worldwide. Its acceptance by the developer communities has been dramatic and places it at the forefront of others languages within this domain (and others). This is evidenced by the large number of Python repositories and tools available on Github alone. A cursory review found that well over 20% of all exploits and attack tools were written in Python.
The chart below sheds clarity on this particular programming phenomenon and the degree to which Python has taken the lead in this domain.
-
The two most popular Python modules used for web-based attacks were “Urllib” and “Requests”. Another newer module “Async IO” is also gaining ground recently as it fits in perfectly for “Layer 7 DDos” type attacks.
-
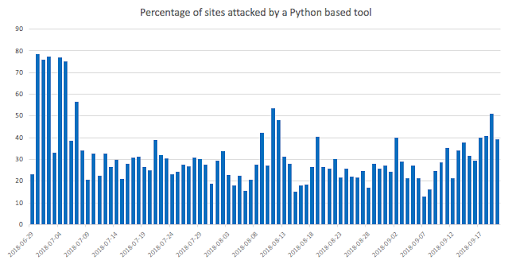
Analysis done on sites that were attacked shows that an alarming 77% were initiated by a Python based tool and in over 30% of cases a Python based tool was responsible for the daily attacks under the APT umbrella.
- Python is also well placed for attack on some of the most popular frameworks used on the web, such as Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, PHP and Struts.
In short, there is ample evidence within business and industry that Python is becoming the de facto language for exploit development and attacks.
Benefits
Organizations need to looking at some of the following steps as a minimum requirement if they are to prevent embarrassing repeat attacks due to VPN vulnerabilities.
-
Ease of Use: Although Python is a high-level language it is still far easier to learn than other languages such as Java, JavaScript, C++, C# etc. This is one of its biggest draws for new developers and young learners evidenced by the sky-high sales of the Raspberry PI for schools and first-time programming students which comes bundled with Python on board. Being so beginner friendly it’s possible to write some basic programs within a few hours of starting your learning path.
-
Open Source: Python is both Free and Open Source and has been available for several platforms (Windows, Mac, Linux etc.) for download from its official website at python.org. The source code is freely available to the public.
-
Interpreted Language: As a high-level language Python is an interpreted language that executes a single line of code instruction at a time. Unlike other languages such as Java, C++ or C# there is no compilation stage to create the executable. This shortens the development time to test new features and changes and is somewhat easier to debug at a line by line level. Python is converted to bytecode at execution time.
-
Portability: Being an interpreted language, Python code has the added benefit of being portable across platforms. Python code developed initially on Windows for example will run “unaltered” on other platforms such as Unix, Linux, Mac etc. In this way the Python programming language really lives up to the axiom of “write once, run everywhere”.
-
Object Oriented: Python comes standard with necessary features for Object Oriented Programming (OOP), supporting classes, inheritance and object/data encapsulation etc. This makes it a lot easier for programmers coming from other languages to jump in quickly and make use of the powerful OOP features that are natively supported within Python.
-
Exploit Writing: Being a general-purpose language Python is used extensively for exploit writing by hackers worldwide. It is the language of choice for millions of hackers and remains the foremost tool for writing exploits, hacking scripts and malware. It would be foolish for any aspiring cyber security student to ignore its importance in this area.
-
Large Standard Library: Python is blessed with a large standard library of functions and modules so that you do not need to reinvent the wheel. Many libraries provide the necessary functionality for web surfing, regular expressions (regex), and unit testing just to name a few. This ready tool belt of functions means a huge step up boost for developers from the get go.
-
Extensibility: Python is by nature an extensible language. The availability of ready-made modules makes hacking easier with Python. Modules are available based on the target audience and platform; OS modules, socket modules, web scraping etc. Python may also be used for socket programming for discovering vulnerabilities in target systems.
-
Huge Community: Python has an enormous community of users, contributors and third-party tool builders. Python has a low entry bar for beginners and provides the perfect tool for writing automation scripts and prototyping ideas quickly and confidently across domains.
Conclusion
For all the reasons above, and some I may have missed, it should be manifestly clear to the reader by now that Python is the language of choice for cyber security professionals. Take the time to do your own research and see how much you can expand your frame of reference by adding a programming language to your tool belt. Just make sure its Python!
References
- Wikipedia Definition: Computer Program
- Most Popular Coding Language: Hackers Weapon of Choice
